#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main() {
std::ios_base::sync_with_stdio(false);
std::cin.tie(NULL);
int cases;
cin >> cases;
int* queue;
int size = 0;
int head = 0, tail = 0;
queue = new int[cases];//case 만큼의 큐 만듦
for (int i = 0; i < cases; i++) {
queue[i] = 0;
}
for (int i = 0; i < cases; i++) {
string command;
cin >> command;
if (command == "push") {
int data;
cin >> data;
if (head != (tail + 1) % cases) {
queue[tail] = data;
tail = (tail + 1) % cases;
size++;
}
}
else if (command == "pop") {
if (size > 0) {
cout << queue[head] << '\n';
head = (head + 1) % cases;
size--;
}
else
cout << -1 << '\n';
}
else if (command == "size") {
cout << size << '\n';
}
else if (command == "empty") {
if (size != 0)
cout << 0 << '\n';
else
cout << 1 << '\n';
}
else if (command == "front") {
if (size > 0)
cout << queue[head] << '\n';
else
cout << -1 << '\n';
}
else if (command == "back") {
if (size > 0)
cout << queue[tail-1] << '\n';
else
cout << -1 << '\n';
}
}
delete[] queue;
return 0;
}
큐는 스택과 반대로 가장 먼저 들어온 자료가 가장 먼저 나간다.(First In First Out)
head와 tail이 있는데, head는 다음에 삭제될 자료의 위치를 가리키고 tail은 다음에 삽입될 자료의 위치를 가리킨다.
데이터가 삽입되고 삭제될 때 마다 head와 tail이 오른쪽으로 이동하는데 메모리 낭비를 방지하기 위해 원형으로 만든다.

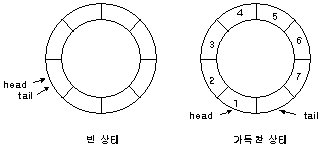
빈 상태에서는 head와 tail이 같은 위치에 있으며 가득찬 상태에서는 tail이 head를 따라잡으면 가득 찬 상태가 된다.
원형이기 때문에 (tail+1)%QueueSize == head 일시 가득 찬 상태이며 tail 부분은 빈 공간으로 남는다.
'백준' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [백준] 2630번 - 분할 정복 알고리즘 (0) | 2022.01.13 |
|---|---|
| [백준] 2750번 - 퀵 정렬 (0) | 2022.01.12 |
| [백준] 10828번 - 스택 기본 (0) | 2022.01.09 |
| [백준] 11047번, 1931번 - 그리디 알고리즘 (0) | 2021.12.31 |
| [백준] 1003번 - 동적 계획법 (0) | 2021.12.30 |

